3 stages of cell cycle gcse Mitosis stages interphase called
The cell cycle is a complex process that takes place in all living organisms, from the smallest bacteria to the largest mammals. It is the process by which cells divide and create new cells, and it consists of three main stages: interphase, mitosis, and cytokinesis. Interphase is the longest stage of the cell cycle, and during this stage, the cell grows and replicates its DNA in preparation for cell division. There are three subphases of interphase: G1, S, and G2. During G1, the cell grows and carries out its normal functions. In S phase, DNA replication occurs, and the cell must ensure that each newly synthesized DNA strand is identical to the original strand. Finally, during G2 phase, the cell checks the replicated DNA for errors and prepares for cell division. Mitosis is the second stage of the cell cycle, and it is the process by which the replicated DNA is divided into two identical sets. There are four stages of mitosis: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During prophase, the replicated chromosomes condense and become visible. During metaphase, the chromosomes align themselves along the equator of the cell. During anaphase, the sister chromatids of each chromosome separate and are pulled towards opposite poles of the cell. Finally, during telophase, the cell divides into two daughter cells. Cytokinesis is the final stage of the cell cycle, and it is the process by which the cell divides into two daughter cells. In animal cells, cytokinesis occurs through the formation of a contractile ring that pinches the cell in two. In plant cells, a cell plate forms at the equator of the cell and separates the cell into two daughter cells. Understanding the cell cycle is crucial for many aspects of biology, including cancer research and regenerative medicine. Cancer is a disease caused by uncontrolled cell division, and many cancer treatments target the cell cycle to stop cancer cells from dividing. Regenerative medicine aims to replace or regenerate damaged or lost tissues and organs, and understanding the cell cycle is crucial for developing new therapies. In summary, the cell cycle consists of three main stages: interphase, mitosis, and cytokinesis. During interphase, the cell grows and replicates its DNA. During mitosis, the DNA is divided into two identical sets. Finally, during cytokinesis, the cell divides into two daughter cells. Understanding the cell cycle is important for many aspects of biology, including cancer research and regenerative medicine.
If you are looking for Introduction to mitosis you’ve came to the right web. We have 5 Images about Introduction to mitosis like 3 Stages Of Cell Cycle Gcse - slide share, 3 Stages Of Cell Cycle Gcse - slide share and also 3 Stages Of Cell Cycle Gcse - slide share. Here you go:
Introduction To Mitosis
 www.slideshare.netmitosis stages interphase called
www.slideshare.netmitosis stages interphase called
3 Stages Of Cell Cycle Gcse - Slide Share
 slidesharetips.blogspot.comcycle ocr division
slidesharetips.blogspot.comcycle ocr division
3 Stages Of Cell Cycle Gcse - Slide Share
 slidesharetips.blogspot.comgcse stages mitosis slide revision minute
slidesharetips.blogspot.comgcse stages mitosis slide revision minute
Cell Cycle Gcse - Google Search | Cell Division, Gcse Science, Cell Cycle
 www.pinterest.comcell cycle gcse division science
www.pinterest.comcell cycle gcse division science
3 Stages Of Cell Cycle Gcse - Slide Share
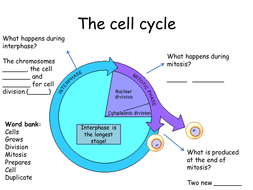
Introduction to mitosis. 3 stages of cell cycle gcse. Cell cycle gcse